Suspected Data Exfiltration by an Employee
🔍 Overview
An employee named John Doe, working in a sensitive department, recently got put on a performance improvement plan (PIP). After John threw a fit, management has raised concerns that John may be planning to steal proprietary information and then quit the company. Your task is to investigate John’s activities on his corporate device (threat-hunting-) using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) and ensure nothing suspicious is taking place. John is an administrator on his device and is not limited on which applications he uses. He may try to archive/compress sensitive information and send it to a private drive or something.
Tools Used
- Cloud Platform: Azure
- EDR: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- SIEM: Microsoft Sentinel
- VM: Windows 10
Scenario 3: Suspected Data Exfiltration by Employee
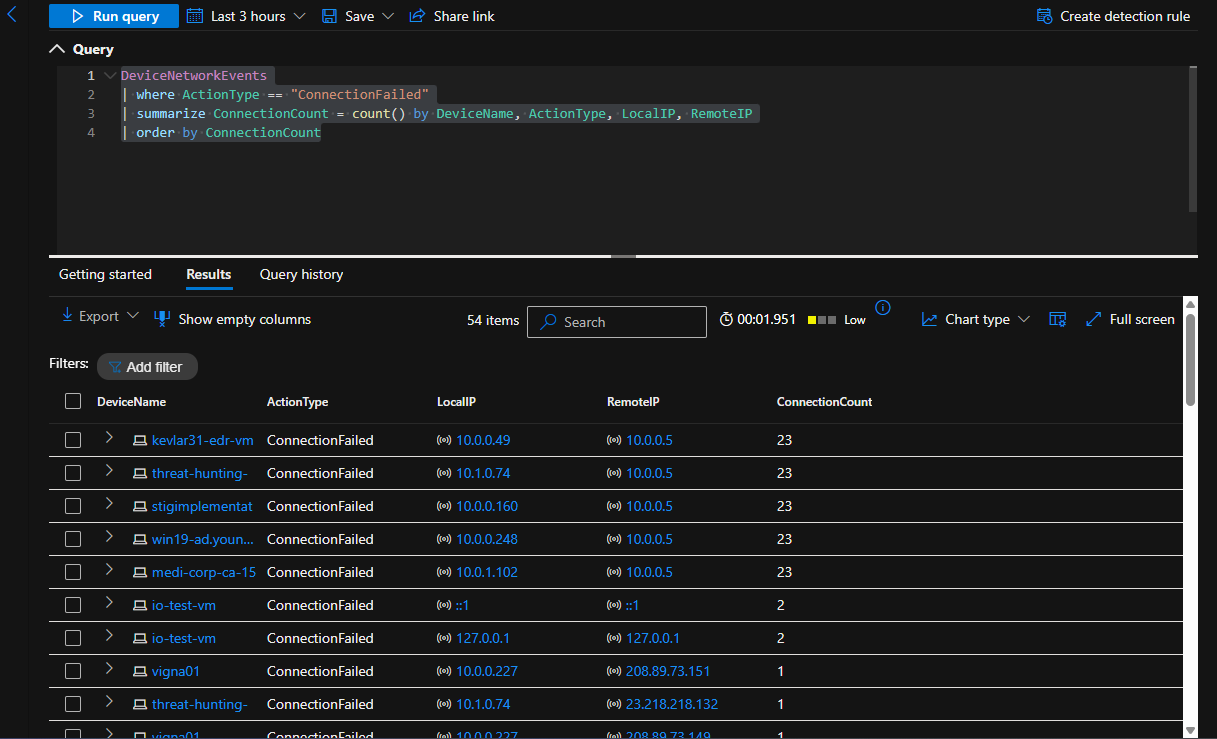
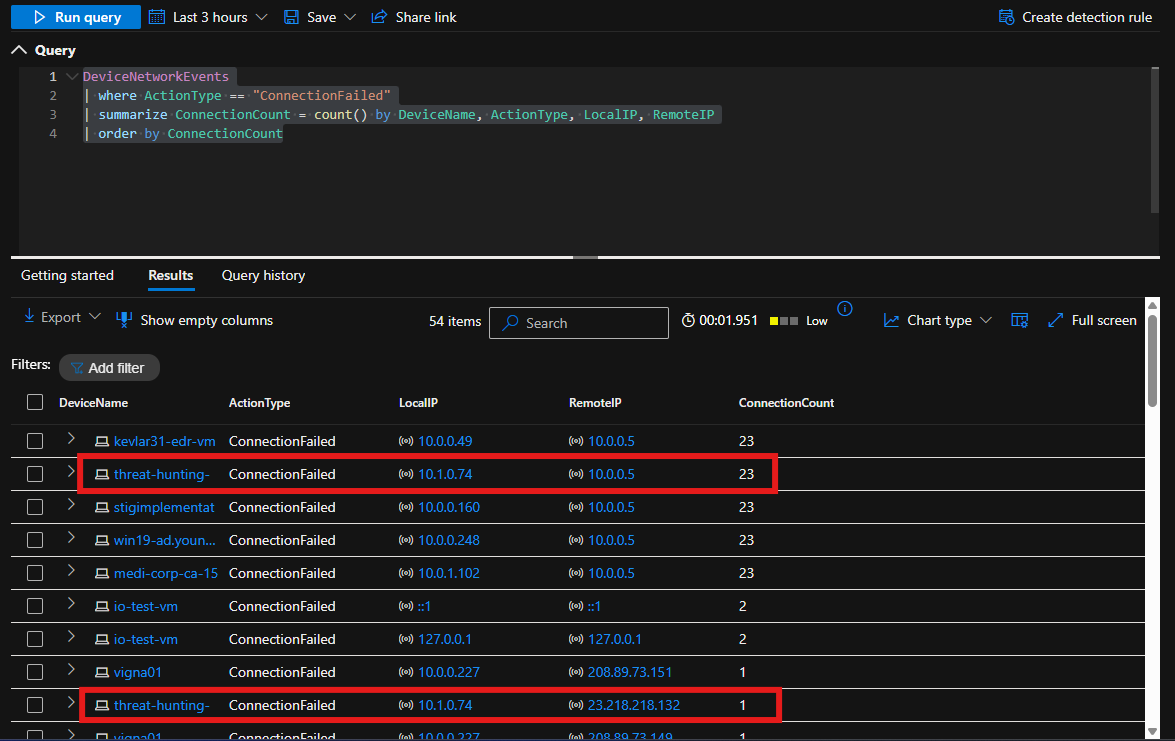
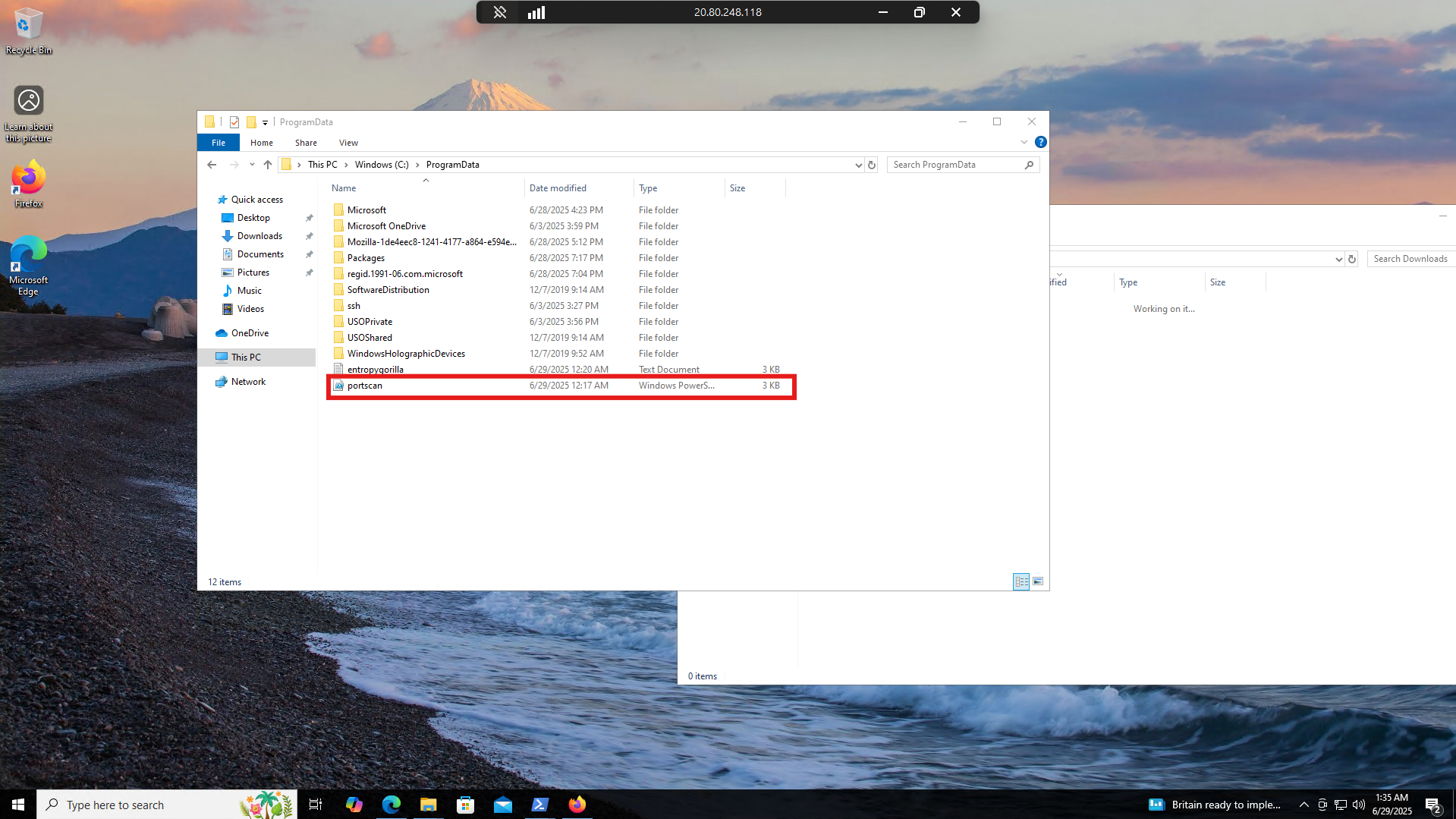
We did a search within MDE DeviceFileEvents for any activities with zip files and found a lot of regular activity of archiving files and moving them to a “backup” folder
1
2
3
4
DeviceFileEvents
| where DeviceName == "threat-hunting-"
| where FileName endswith ".zip"
| order by Timestamp desc
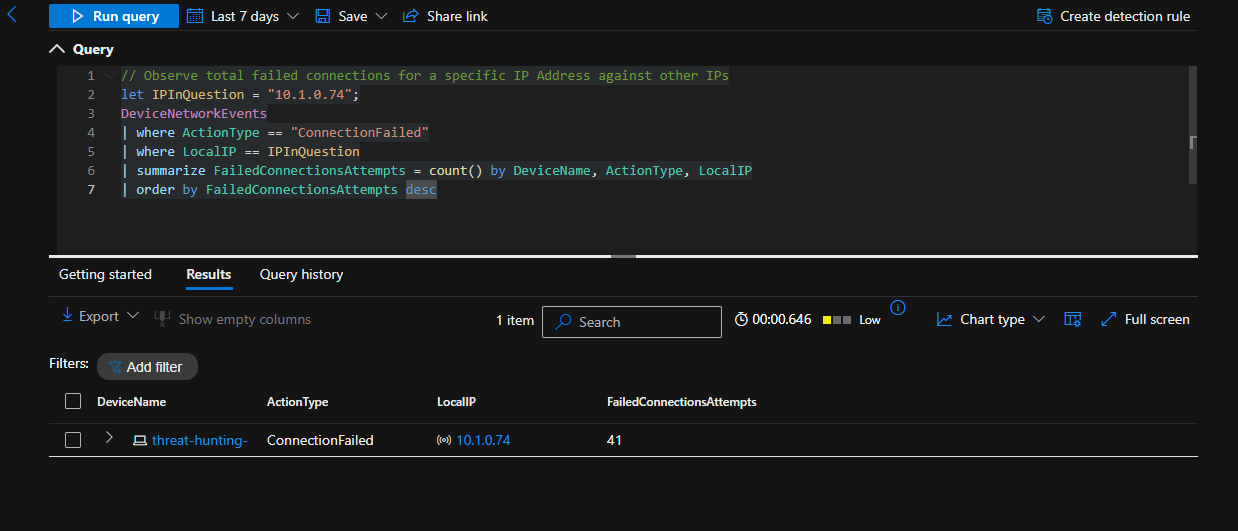
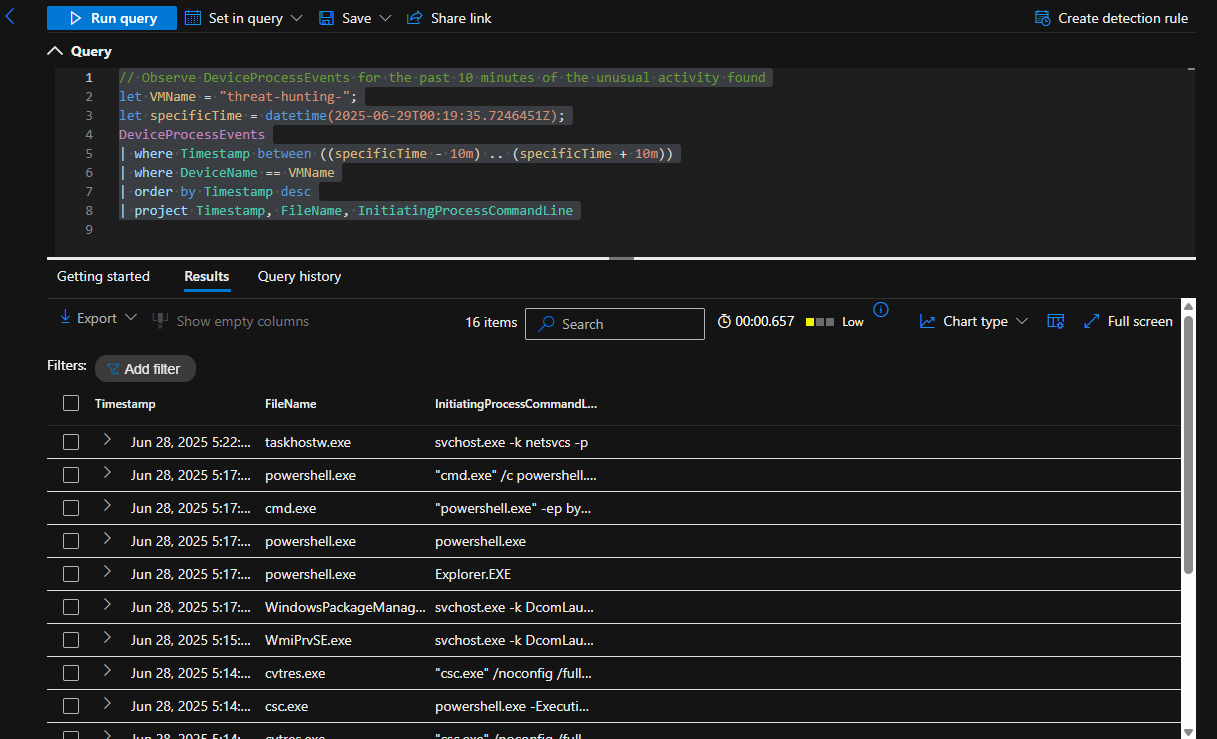
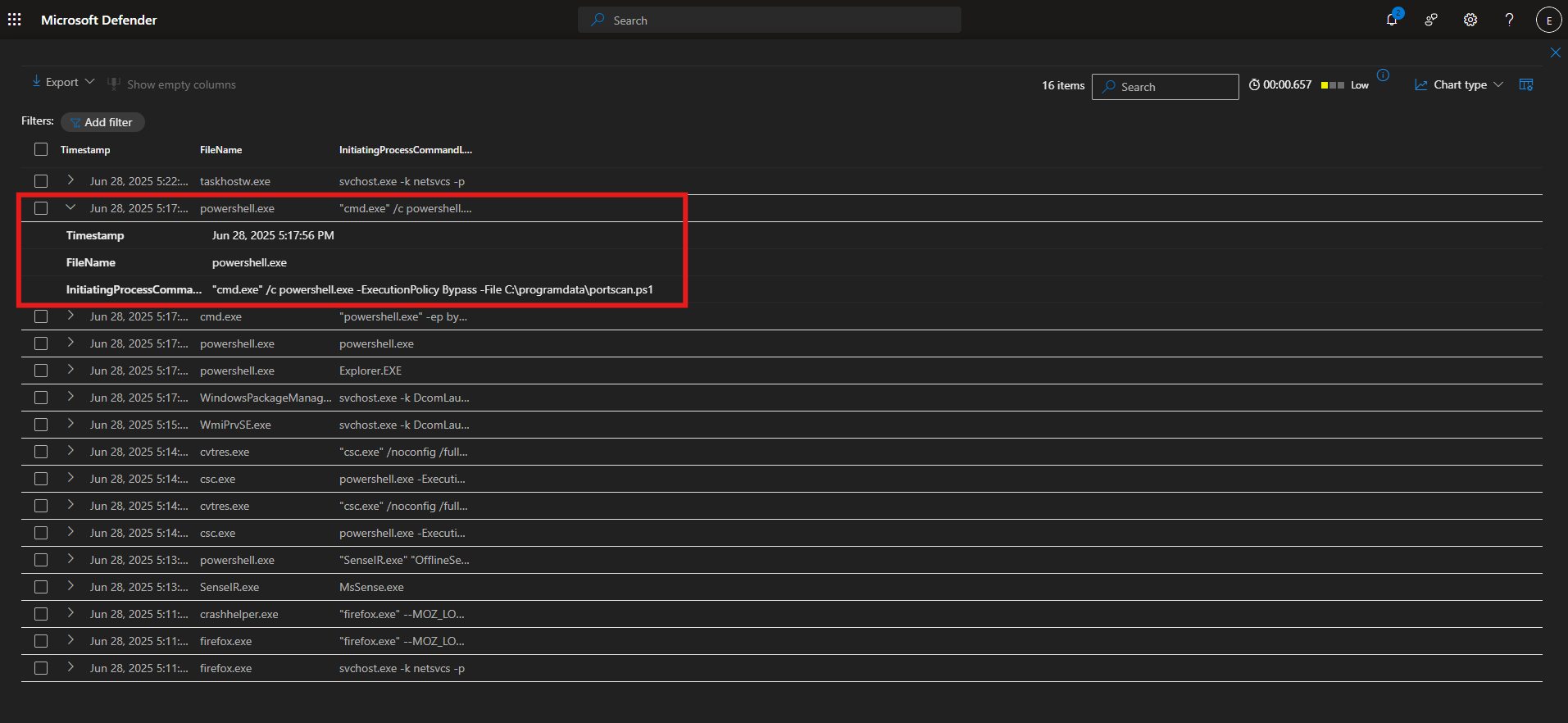
I took one of the instances of the zip file that was created, took the timestamp, and searched under DeviceProcessEvents for anything happening 2 minutes before the archive was created and 2 minutes after. I discovered around the same time, a powershell script silently installed 7zip and used 7zip to zip up employee data into an archive.
Look for any file activity, based on the Timestamp from any discovered process activity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// Look for any file activity, based on the Timestamp from any discovered process activity
let specificTime = datetime(2025-06-29T03:41:29.5740699Z);
let VMName = "threat-hunting-";
DeviceFileEvents
| where Timestamp between ((specificTime - 2m) .. (specificTime + 2m))
| where DeviceName == VMName
| order by Timestamp desc
Digging Deeper
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
let specificTime = datetime(2025-06-29T03:41:29.5740699Z);
let VMName = "threat-hunting-";
DeviceFileEvents
| where Timestamp between ((specificTime - 2m) .. (specificTime + 2m))
| where DeviceName == VMName
| order by Timestamp desc
| project Timestamp, DeviceName, ActionType, FileName, InitiatingProcessCommandLine
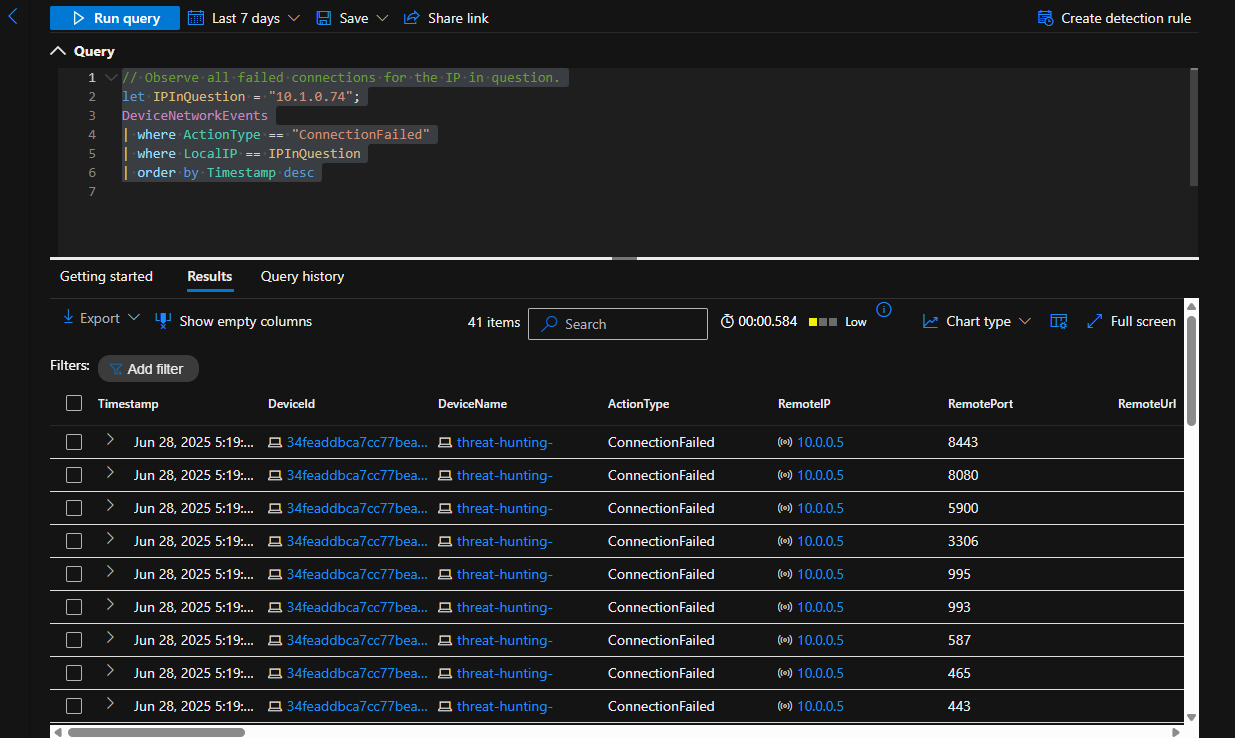
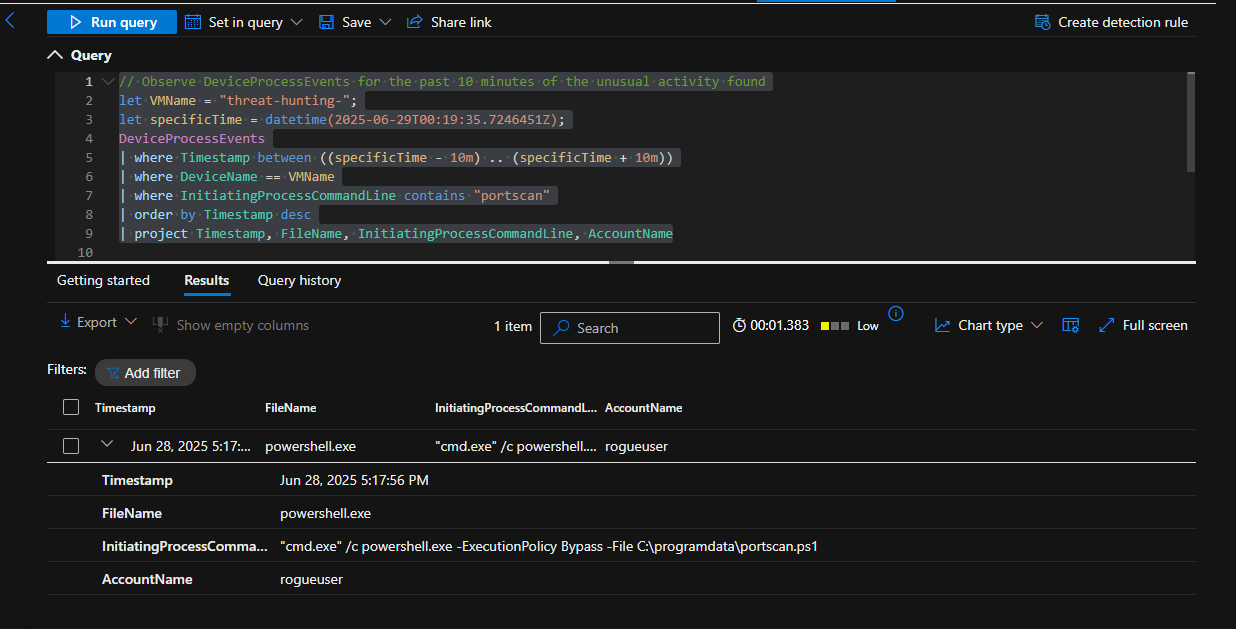
I searched around the same time period for any evidence of exfiltration from the network, but I didn’t see any logs indicating as such:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
let specificTime = datetime(2025-06-29T03:45:24.1058031Z);
let VMName = "threat-hunting-";
DeviceNetworkEvents
| where Timestamp between ((specificTime - 4m) .. (specificTime + 4m))
| where DeviceName == VMName
| order by Timestamp desc
| project Timestamp, DeviceName, ActionType, InitiatingProcessCommandLine
Response:
I relayed the information to the employee’s manager, including everything with the archives being created at regular intervals via PowerShell script. There did not appear to be any evidence of exfiltration, but it’s worth bringing up to the employee. Standing by for further instructions from management.
MITRE ATT&CK Framework TTPs:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
T1059.001 – Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell
> PowerShell was used to silently install and run 7-Zip for archiving files.
T1560.001 – Archive Collected Data: Archive via Utility
> 7-Zip was used to compress employee data into `.zip` files.
T1074.001 – Data Staged: Local Data Staging
> Archived data was moved to a “backup” folder, indicating local staging prior to potential exfiltration.
T1204.002 – User Execution: Malicious File
> (Possible) If the PowerShell script was user-executed or placed by the user without IT approval.
T1036 – Masquerading
> Installing and using 7-Zip silently could indicate an attempt to blend in with legitimate tools or bypass user detection.
T1005 – Data from Local System
> The employee accessed and collected local data before archiving.
T1105 – Ingress Tool Transfer
> (Possible) If 7-Zip was downloaded from the internet and silently installed during the PowerShell session.
Mitigations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
M1038 – Execution Prevention
> Prevent or restrict execution of PowerShell scripts and unauthorized software installations (like 7-Zip) using application control solutions (e.g., AppLocker, WDAC).
M1021 – Restrict Web-Based Content
> Block access to unauthorized download sites that may host tools like 7-Zip using web content filtering or DNS-layer security.
M1040 – Behavior Prevention on Endpoint
> Use endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to detect unusual file archiving, scripting behavior, and non-standard software installations.
M1042 – Disable or Remove Feature or Program
> Disable or restrict the use of PowerShell for non-administrative users if not needed, and remove unnecessary utilities like 7-Zip if not required for business operations.
M1054 – Software Configuration
> Configure PowerShell to run in **Constrained Language Mode** and enable **Script Block Logging** and **Module Logging** for better auditing.
M1022 – Restrict File and Directory Permissions
> Apply least privilege to file directories. Prevent users from accessing or archiving sensitive data without proper justification or permissions.
M1049 – Antivirus/Antimalware
> Ensure antivirus/antimalware solutions are in place and can detect unauthorized software installations or suspicious archive creation.
M1032 – Multi-factor Authentication
> Ensure the user account associated with the behavior is protected with MFA to reduce the risk of account misuse or lateral movement.
Isolating Device
We can create a detection rule to find if any zip files have a suspiciously high amount of activity
1
2
3
4
DeviceFileEvents
| where FileName endswith ".zip"
| summarize ZipFileActivity = count() by RequestAccountName
| where ZipFileActivity > 50