New Zero-Day Announced on News
🔍 Overview
A new ransomware strain named PwnCrypt has been reported in the news, leveraging a PowerShell-based payload to encrypt files on infected systems. The payload, using AES-256 encryption, targets specific directories such as the C:\Users\Public\Desktop, encrypting files and prepending a .pwncrypt extension to the original extension. For example, hello.txt becomes hello.pwncrypt.txt after being targeted with the ransomware. The CISO is concerned with the new ransomware strain being spread to the corporate network and wishes to investigate.
Tools Used
- Cloud Platform: Azure
- EDR: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- SIEM: Microsoft Sentinel
- VM: Windows 10
Scenario 4: New Zero-Day Announced on News
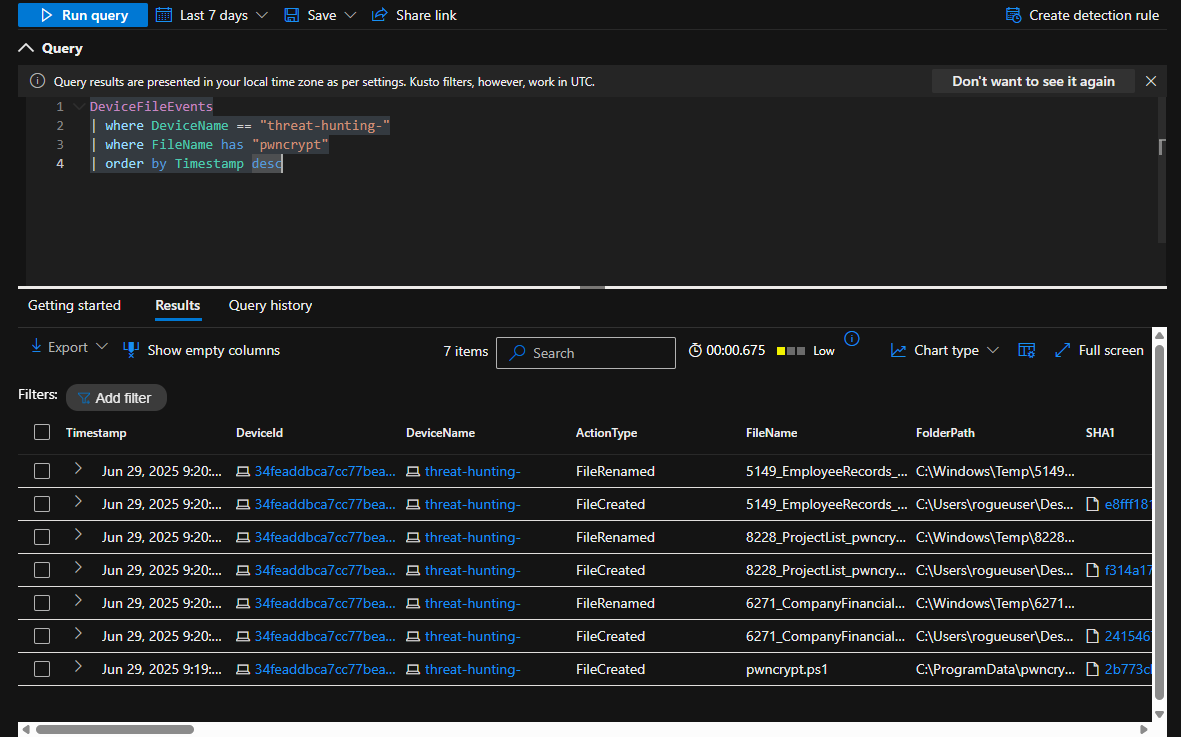
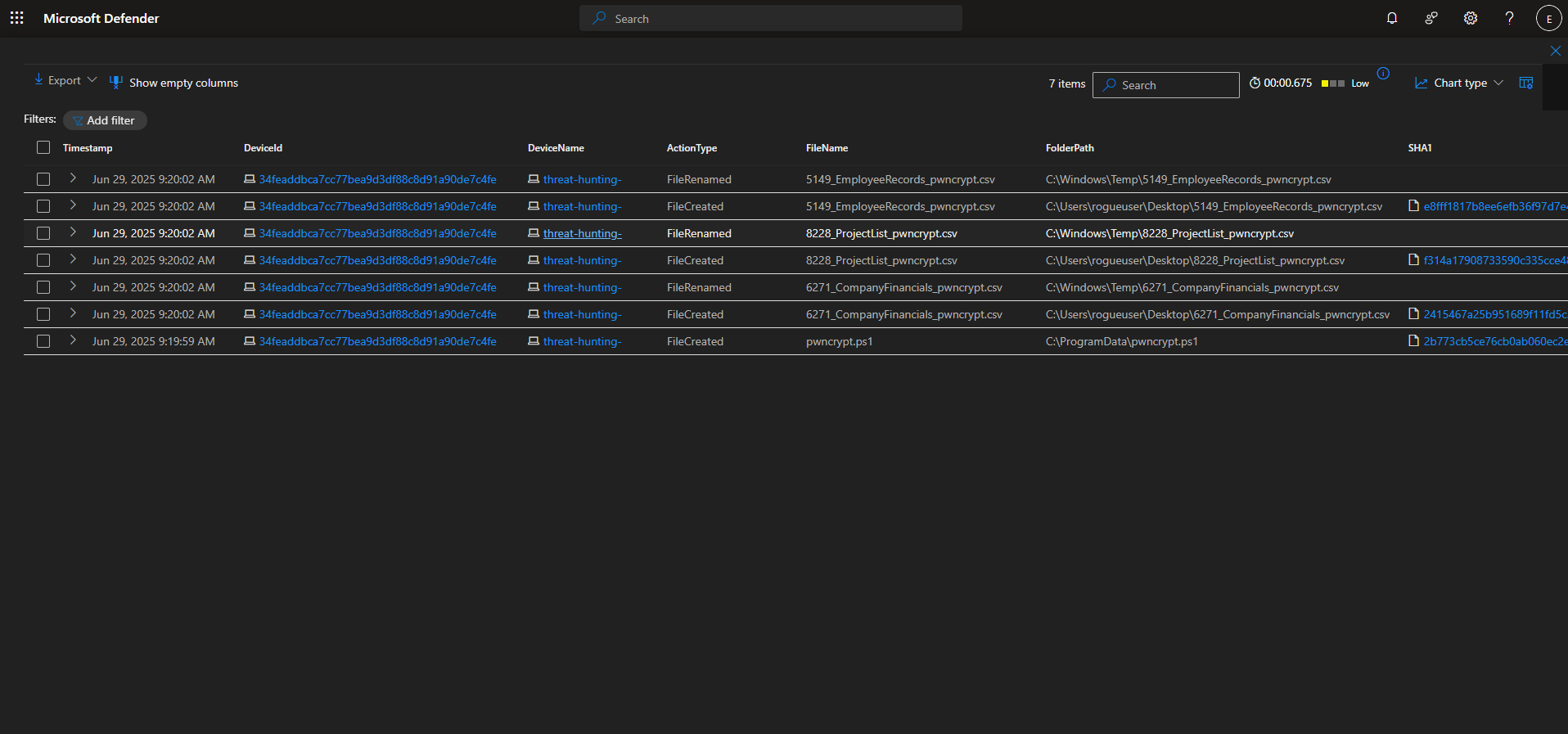
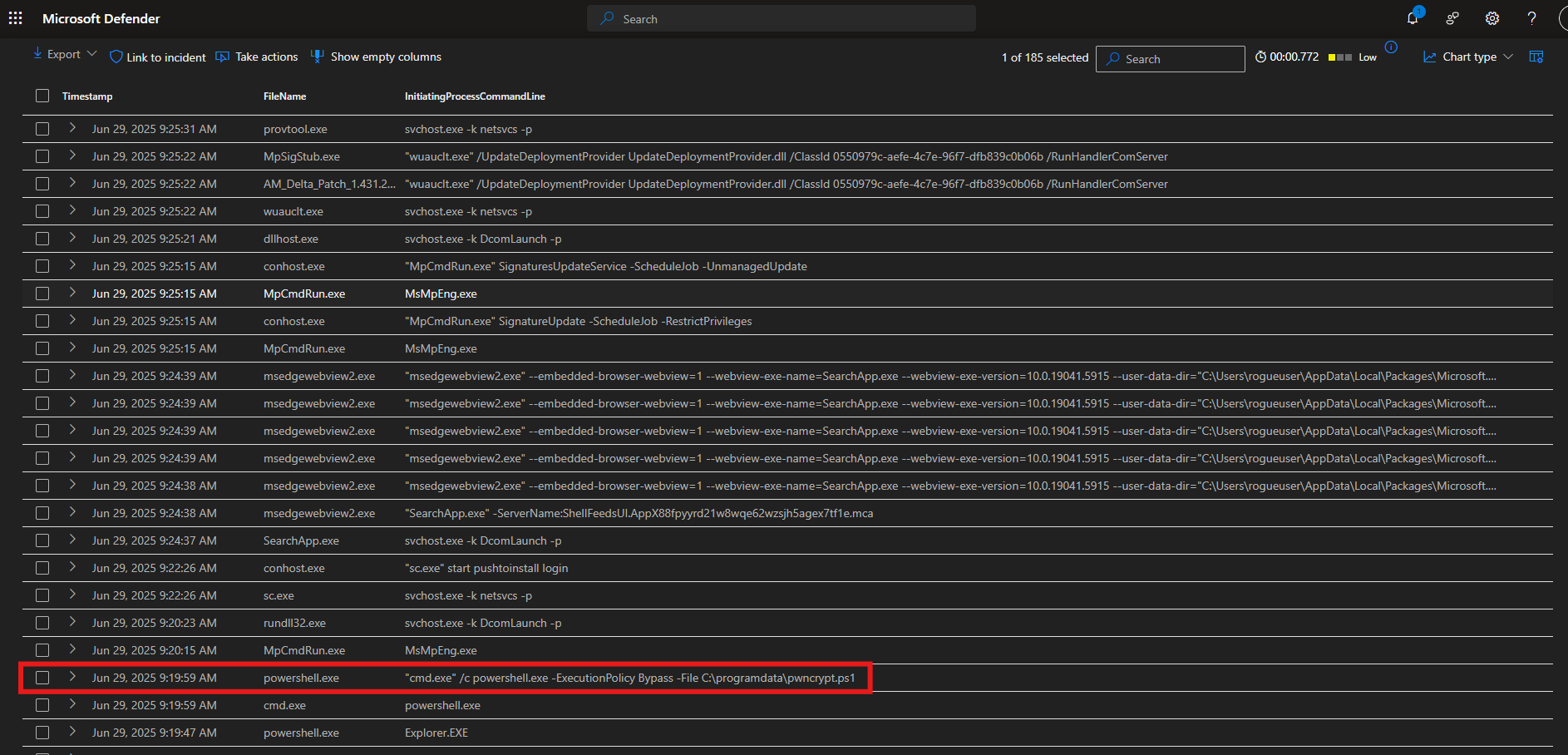
Searching for filenames that include the string “pwncrypt” on the machine “threat-hunting-”
1
2
3
4
DeviceFileEvents
| where DeviceName == "threat-hunting-"
| where FileName has "pwncrypt"
| order by Timestamp desc
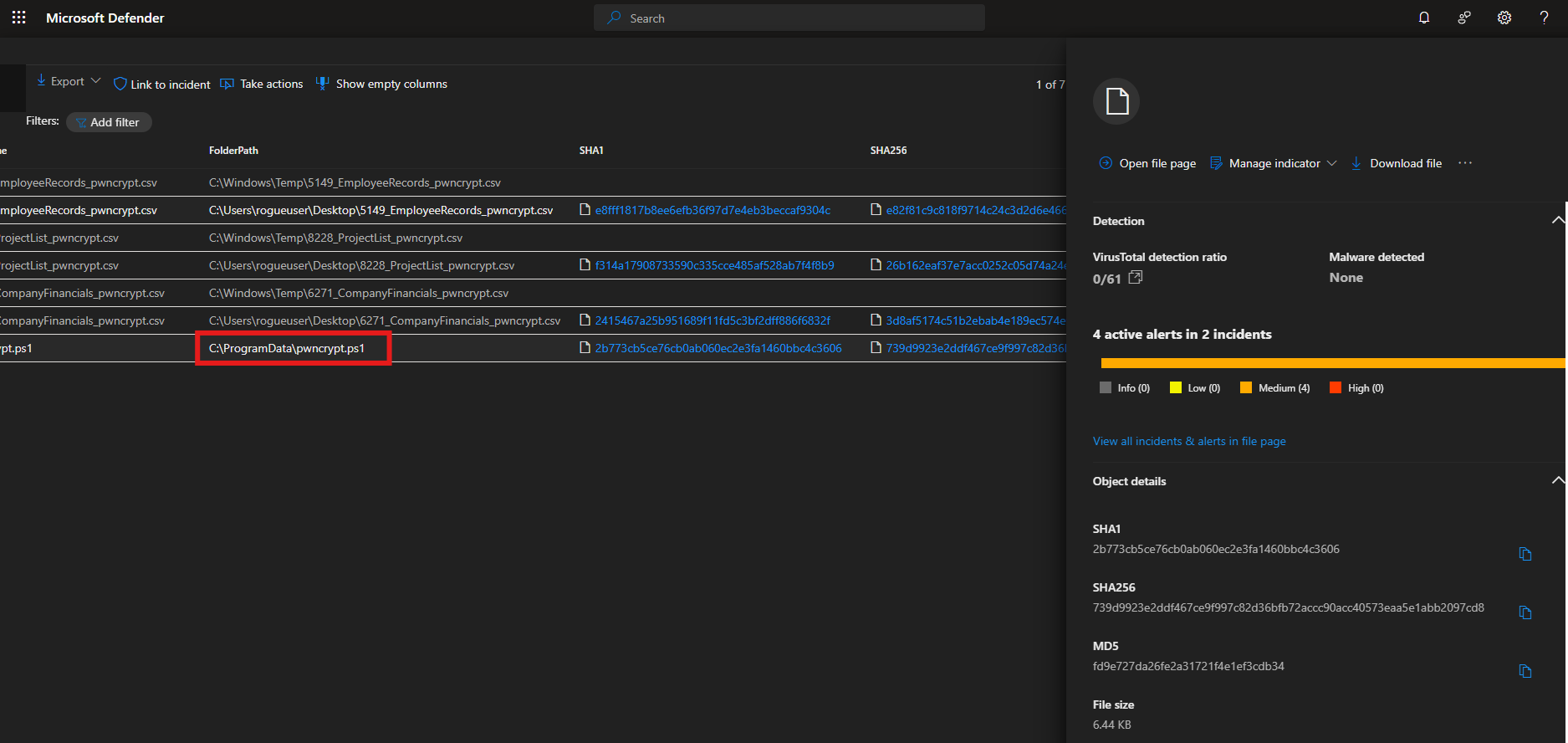
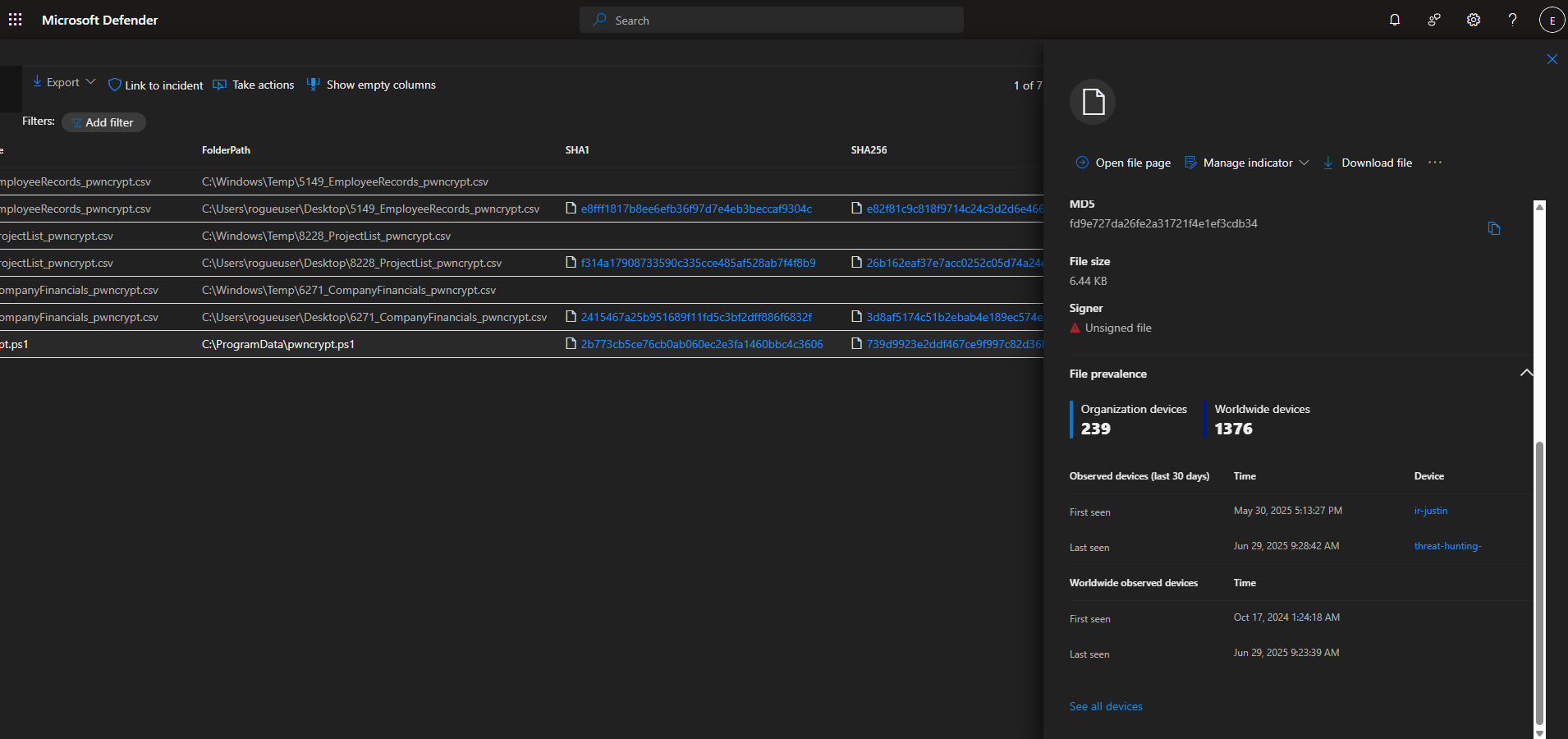
FILE HASHES: pwncrypt.ps1
SHA1
1
2b773cb5ce76cb0ab060ec2e3fa1460bbc4c3606
SHA256
1
739d9923e2ddf467ce9f997c82d36bfb72accc90acc40573eaa5e1abb2097cd8
MD5
1
fd9e727da26fe2a31721f4e1ef3cdb34
VirusTotal Search Results using MD5 Hash:
VirusTotal Page for MD5 Hash Results
Observe DeviceProcessEvents for the past 10 minutes of the unusual activity found
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// Observe DeviceProcessEvents for the past 10 minutes of the unusual activity found
let VMName = "threat-hunting-";
let specificTime = datetime(2025-06-29T16:20:02.98804Z);
DeviceProcessEvents
| where Timestamp between ((specificTime - 10m) .. (specificTime + 10m))
| where DeviceName == VMName
| order by Timestamp desc
| project Timestamp, FileName, InitiatingProcessCommandLine
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
T1059.001 – Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell
> The filename `pwncrypt.ps1` suggests the use of PowerShell to execute malicious or post-exploitation scripts.
T1204.002 – User Execution: Malicious File
> If the script was executed by a user (manually or via phishing lure), it may align with user execution tactics.
T1027 – Obfuscated Files or Information
> PowerShell scripts used for malicious purposes are often obfuscated to bypass detection. Further inspection of the script may confirm this.
T1566.001 – Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment
> (Possible) If the file was delivered via email and the user ran it, this delivery vector is likely.
T1105 – Ingress Tool Transfer
> If the script was downloaded from a C2 server or public repo during the session, this technique applies.
T1036 – Masquerading
> The script name (`pwncrypt.ps1`) may try to resemble legitimate scripts or imply a ransomware payload while hiding true intent.
T1112 – Modify Registry
> If post-execution analysis shows persistence mechanisms or PowerShell registry modifications, this TTP may also apply.
T1055 – Process Injection *(possible, based on future analysis)*
> If the script performs process injection, this technique could apply as a follow-up.
Mitigations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
M1038 – Execution Prevention
> Block unauthorized script execution with AppLocker or WDAC policies that restrict `.ps1` files to approved paths and signers.
M1040 – Behavior Prevention on Endpoint
> Use EDR/XDR tools to alert on anomalous script activity or execution of files with suspicious naming conventions.
M1042 – Disable or Remove Feature or Program
> Restrict PowerShell to Constrained Language Mode for non-admin users. Remove or lock down PowerShell where not required.
M1054 – Software Configuration
> Enable PowerShell logging: Script Block Logging, Module Logging, and Transcription to monitor and record script execution.
M1021 – Restrict Web-Based Content
> Block downloading of scripts and tools from non-corporate or suspicious domains using DNS filtering or secure web gateways.
M1022 – Restrict File and Directory Permissions
> Prevent users from writing or executing scripts in sensitive or admin-level directories.
M1031 – Network Segmentation
> Isolate suspicious endpoints quickly from the rest of the network to prevent lateral movement or data staging.
M1032 – Multi-Factor Authentication
> Protect all administrative accounts with MFA to reduce privilege abuse or attacker persistence.
M1037 – Filter Network Traffic
> Monitor or restrict traffic associated with common PowerShell download commands (e.g., `Invoke-WebRequest`, `Invoke-Expression`).
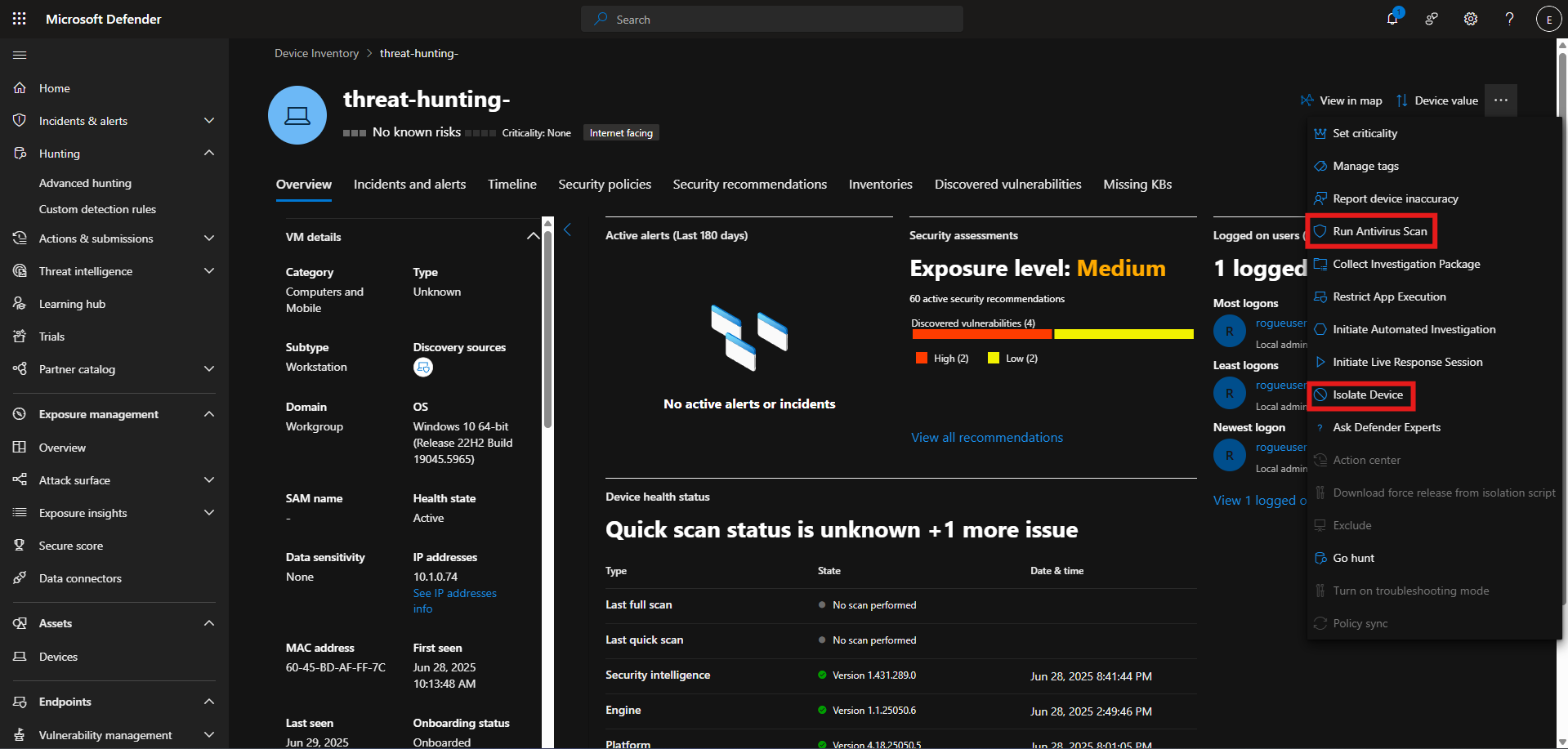
Isolate the Device and run an Antivirus Scan