Sudden Network Slowdowns
🔍 Overview
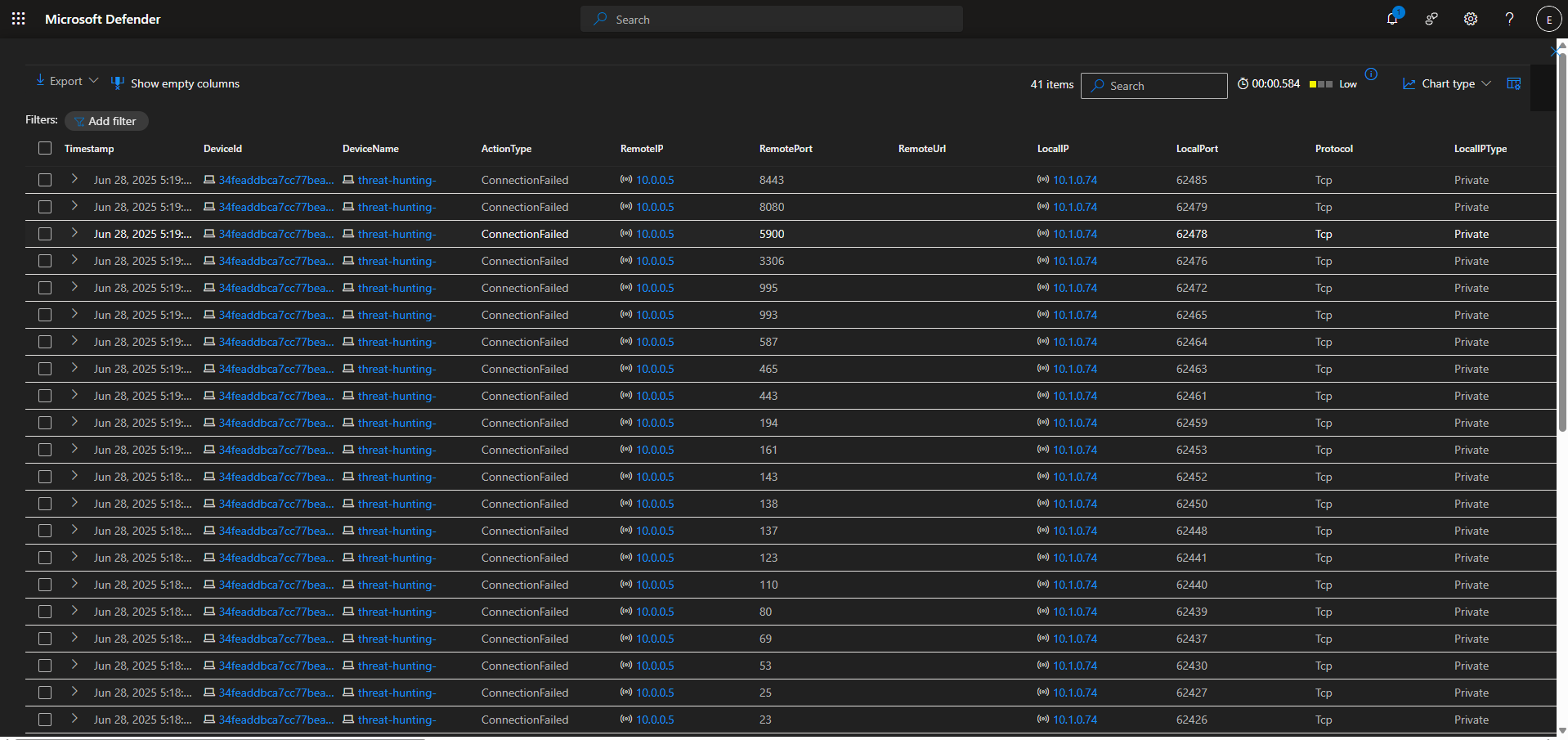
The server team has noticed a significant network performance degradation on some of their older devices attached to the network in the 10.0.0.0/16 network. After ruling out external DDoS attacks, the security team suspects something might be going on internally. Machine Threat-Hunting- was found failing several connection requests against windows-target-1 and another host on the same network
Tools Used
- Cloud Platform: Azure
- EDR: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- SIEM: Microsoft Sentinel
- VM: Windows 10
Scenario 2: Sudden Network Slowdowns
Machine Threat-Hunting- was found failing several connection requests against windows-target-1 and another host on the same network:
1
2
3
4
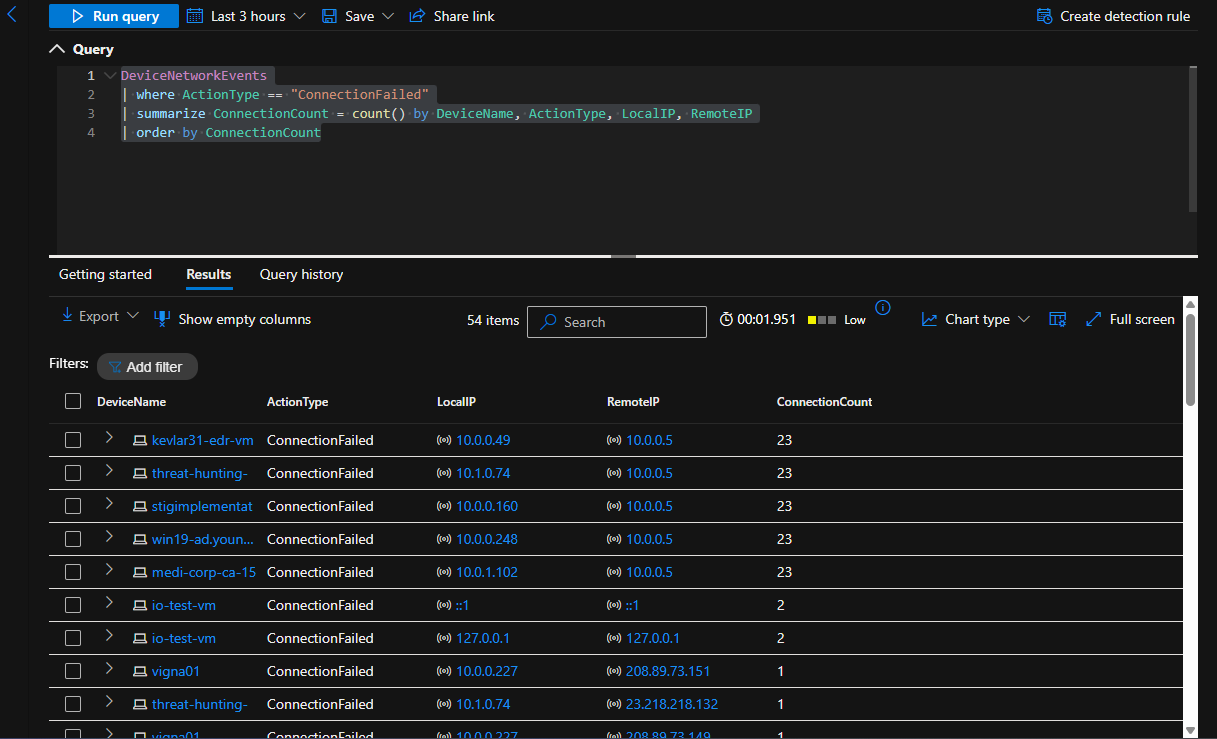
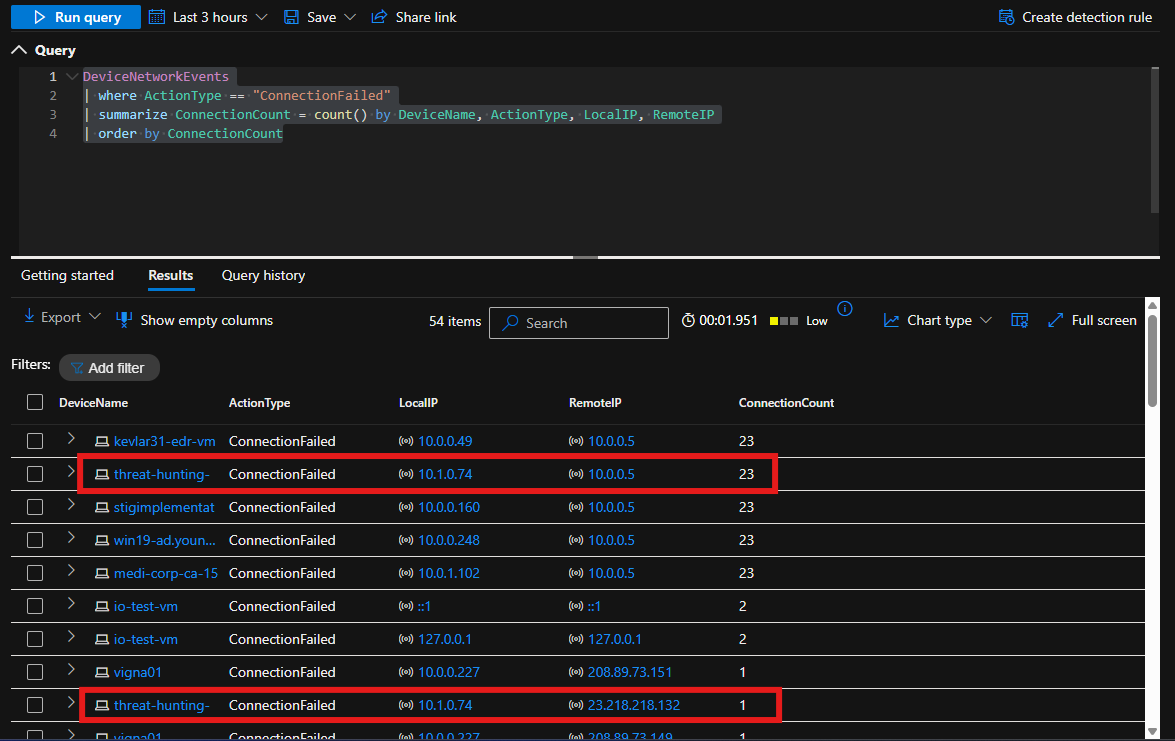
DeviceNetworkEvents
| where ActionType == "ConnectionFailed"
| summarize ConnectionCount = count() by DeviceName, ActionType, LocalIP, RemoteIP
| order by ConnectionCount
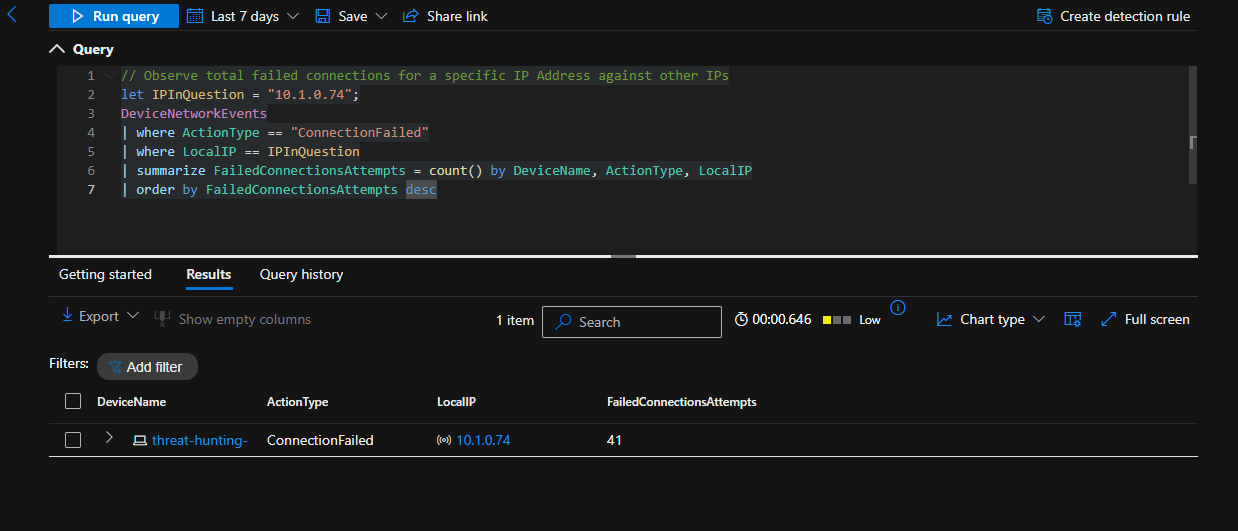
Observe total failed connections for a specific IP Address against other IPs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// Observe total failed connections for a specific IP Address against other IPs
let IPInQuestion = "10.1.0.74";
DeviceNetworkEvents
| where ActionType == "ConnectionFailed"
| where LocalIP == IPInQuestion
| summarize FailedConnectionsAttempts = count() by DeviceName, ActionType, LocalIP
| order by FailedConnectionsAttempts desc
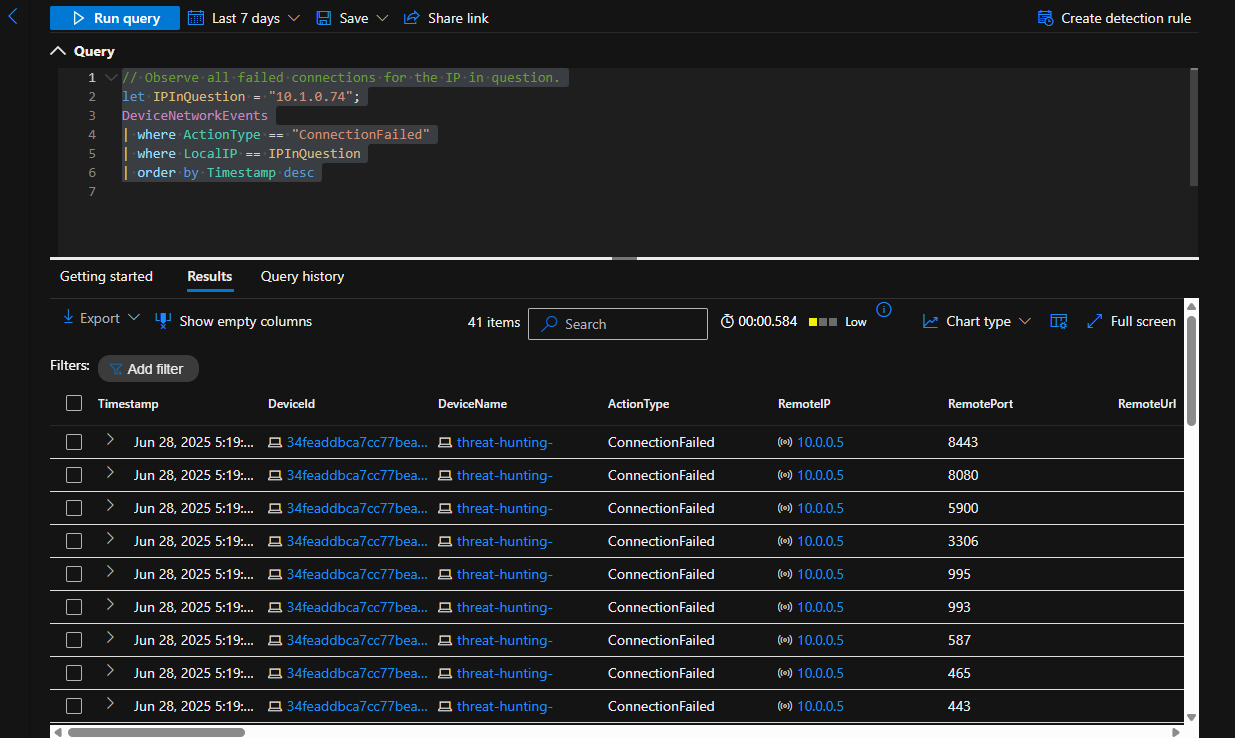
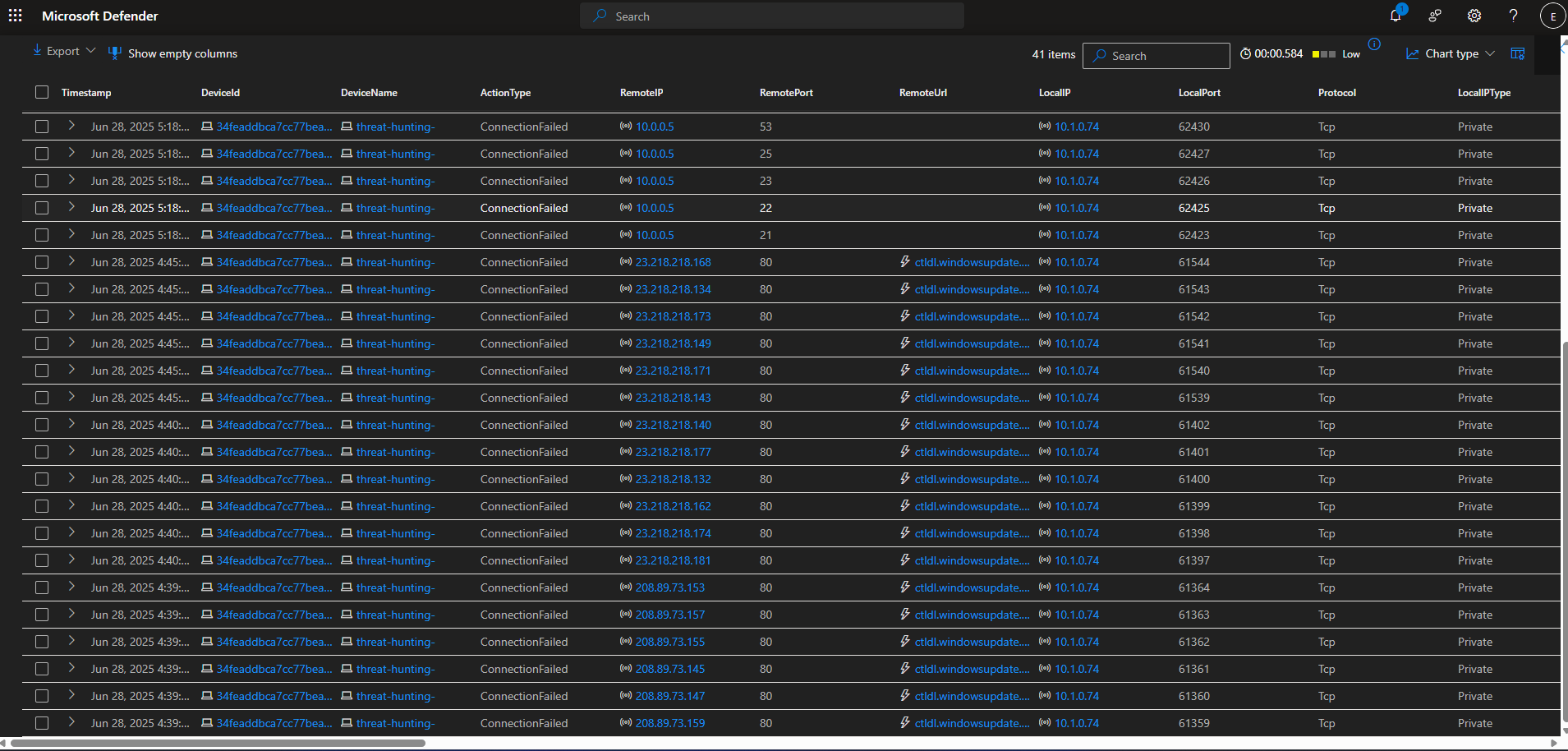
Observe all failed connections for the IP in question.
1
2
3
4
5
6
// Observe all failed connections for the IP in question.
let IPInQuestion = "10.1.0.74";
DeviceNetworkEvents
| where ActionType == "ConnectionFailed"
| where LocalIP == IPInQuestion
| order by Timestamp desc
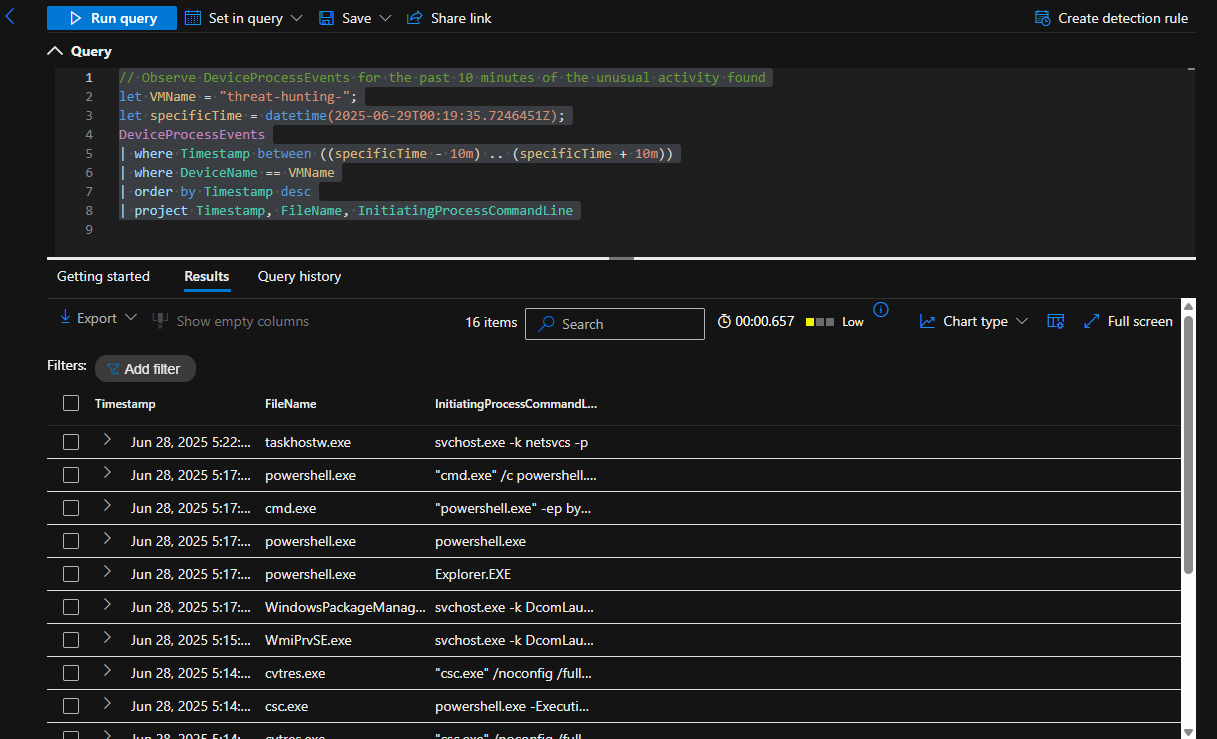
Observe DeviceProcessEvents for the past 10 minutes of the unusual activity found
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// Observe DeviceProcessEvents for the past 10 minutes of the unusual activity found
let VMName = "threat-hunting-";
let specificTime = datetime(2025-06-29T00:19:35.7246451Z);
DeviceProcessEvents
| where Timestamp between ((specificTime - 10m) .. (specificTime + 10m))
| where DeviceName == VMName
| order by Timestamp desc
| project Timestamp, FileName, InitiatingProcessCommandLine
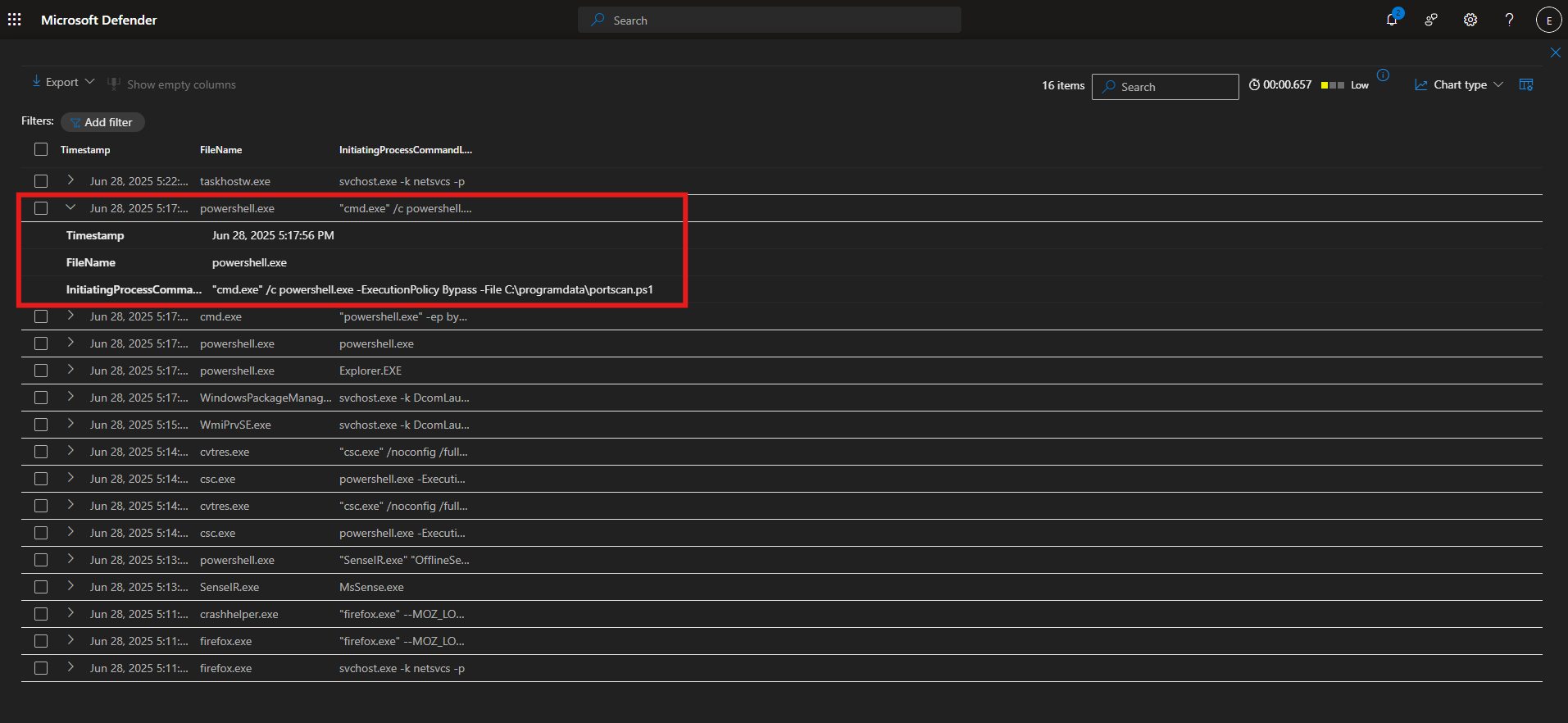
After observing failed conection requests from our suspected host (10.1.0.74) in chronological order, I noticed a port scan was taking place due to the sequential order of the ports. There were several port scans being conducted
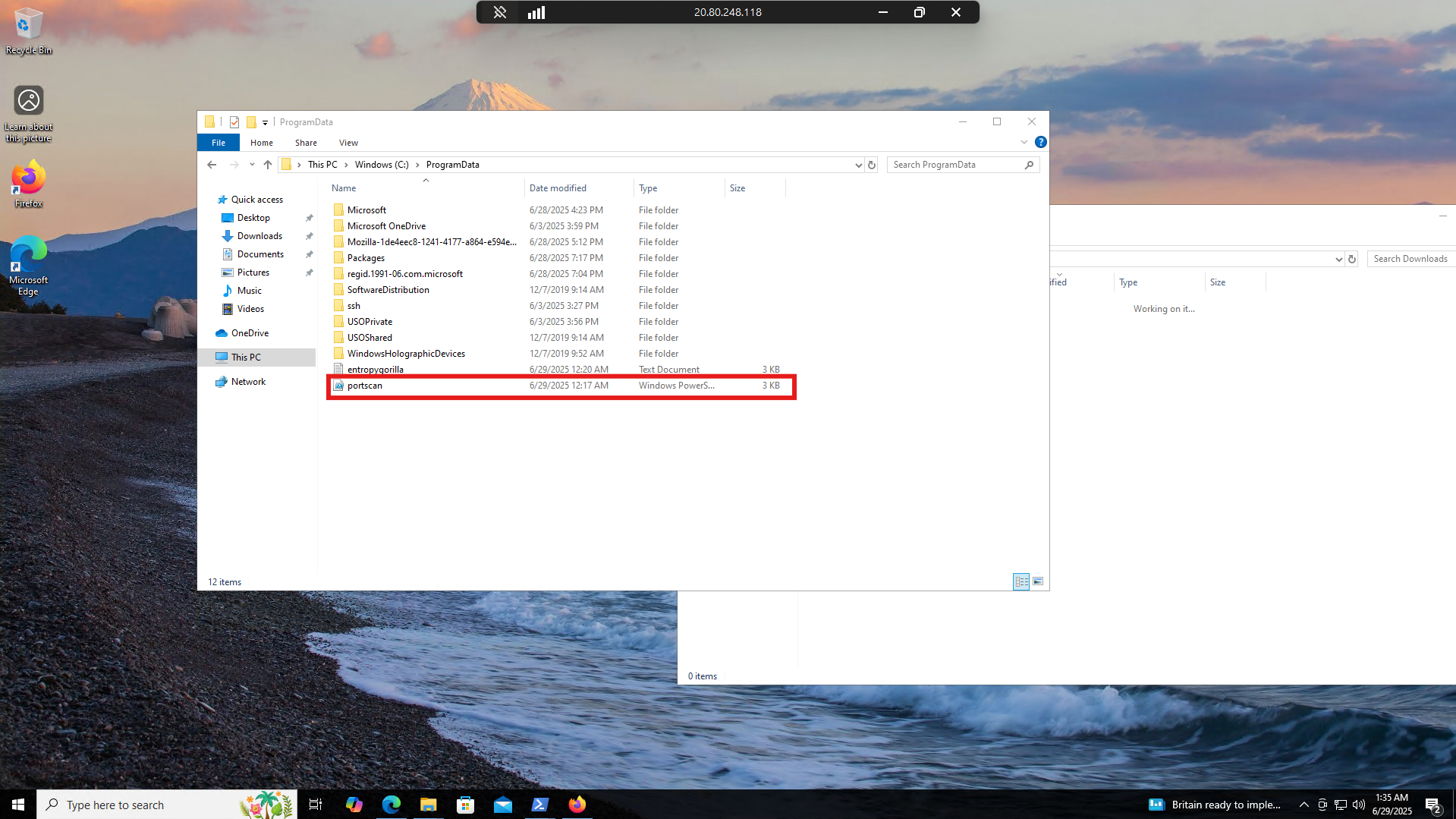
I logged into the suspected computer and observed the PowerShell script that was used to conduct the port scan.
FILE: portscan.ps1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
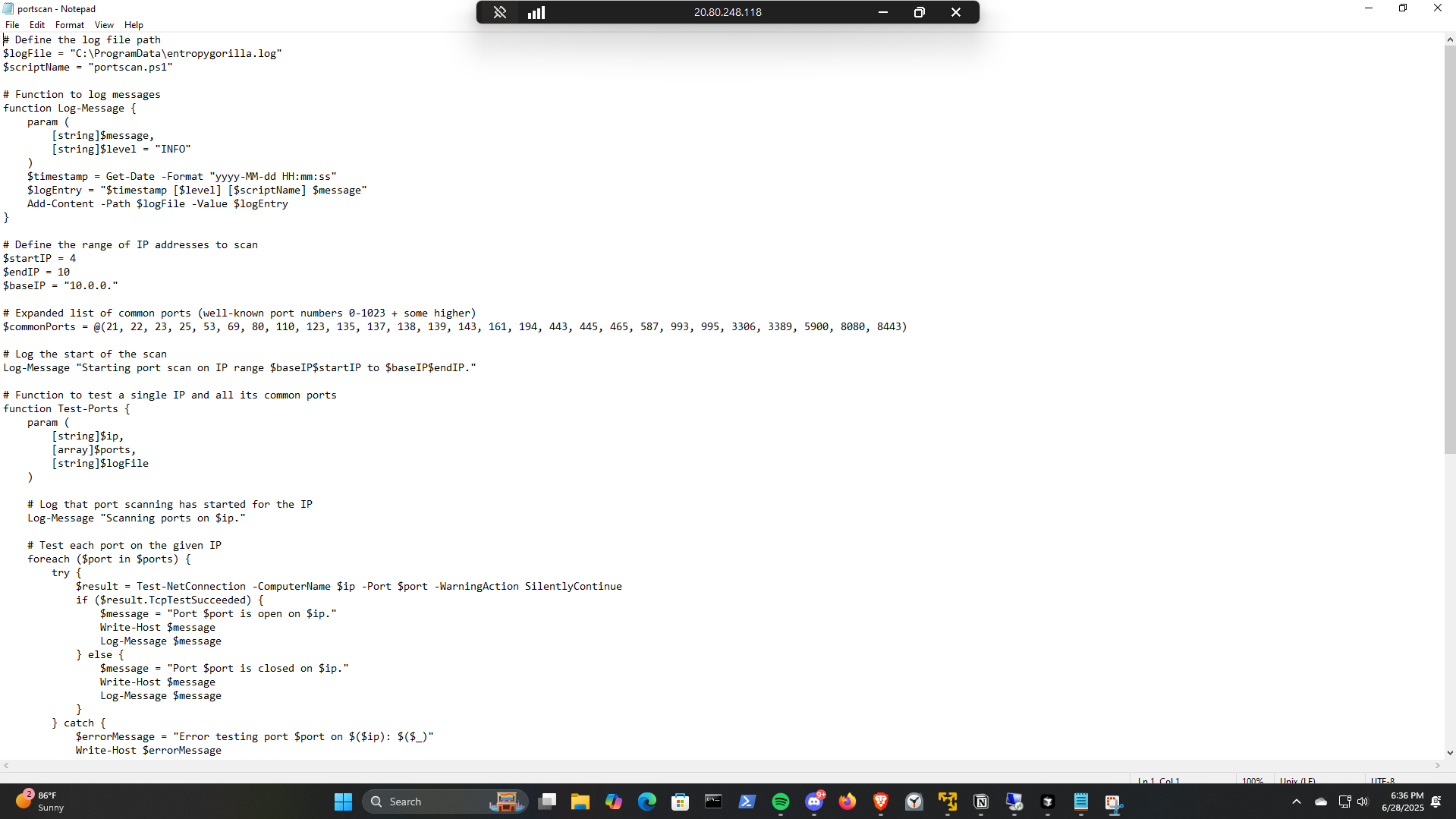
# Define the log file path
$logFile = "C:\ProgramData\entropygorilla.log"
$scriptName = "portscan.ps1"
# Function to log messages
function Log-Message {
param (
[string]$message,
[string]$level = "INFO"
)
$timestamp = Get-Date -Format "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
$logEntry = "$timestamp [$level] [$scriptName] $message"
Add-Content -Path $logFile -Value $logEntry
}
# Define the range of IP addresses to scan
$startIP = 4
$endIP = 10
$baseIP = "10.0.0."
# Expanded list of common ports (well-known port numbers 0-1023 + some higher)
$commonPorts = @(21, 22, 23, 25, 53, 69, 80, 110, 123, 135, 137, 138, 139, 143, 161, 194, 443, 445, 465, 587, 993, 995, 3306, 3389, 5900, 8080, 8443)
# Log the start of the scan
Log-Message "Starting port scan on IP range $baseIP$startIP to $baseIP$endIP."
# Function to test a single IP and all its common ports
function Test-Ports {
param (
[string]$ip,
[array]$ports,
[string]$logFile
)
# Log that port scanning has started for the IP
Log-Message "Scanning ports on $ip."
# Test each port on the given IP
foreach ($port in $ports) {
try {
$result = Test-NetConnection -ComputerName $ip -Port $port -WarningAction SilentlyContinue
if ($result.TcpTestSucceeded) {
$message = "Port $port is open on $ip."
Write-Host $message
Log-Message $message
} else {
$message = "Port $port is closed on $ip."
Write-Host $message
Log-Message $message
}
} catch {
$errorMessage = "Error testing port $port on $($ip): $($_)"
Write-Host $errorMessage
Log-Message $errorMessage "ERROR"
}
}
# Log that port scanning has finished for the IP
Log-Message "Finished scanning ports on $ip."
}
# Loop through each IP in the range
for ($i = $startIP; $i -le $endIP; $i++) {
$ip = $baseIP + $i
try {
# Test connectivity using Test-NetConnection (ICMP ping)
$ping = Test-NetConnection -ComputerName $ip -WarningAction SilentlyContinue
if ($ping.PingSucceeded) {
$message = "$ip is online."
Write-Host $message
Log-Message $message
# Scan all ports on the online host sequentially (no threads)
Test-Ports -ip $ip -ports $commonPorts -logFile $logFile
} else {
$message = "$ip is offline."
Write-Host $message
Log-Message $message
}
} catch {
$errorMessage = "Error testing $($ip): $($_)"
Write-Host $errorMessage
Log-Message $errorMessage "ERROR"
}
}
# Log the end of the scan
Log-Message "Port scan completed."
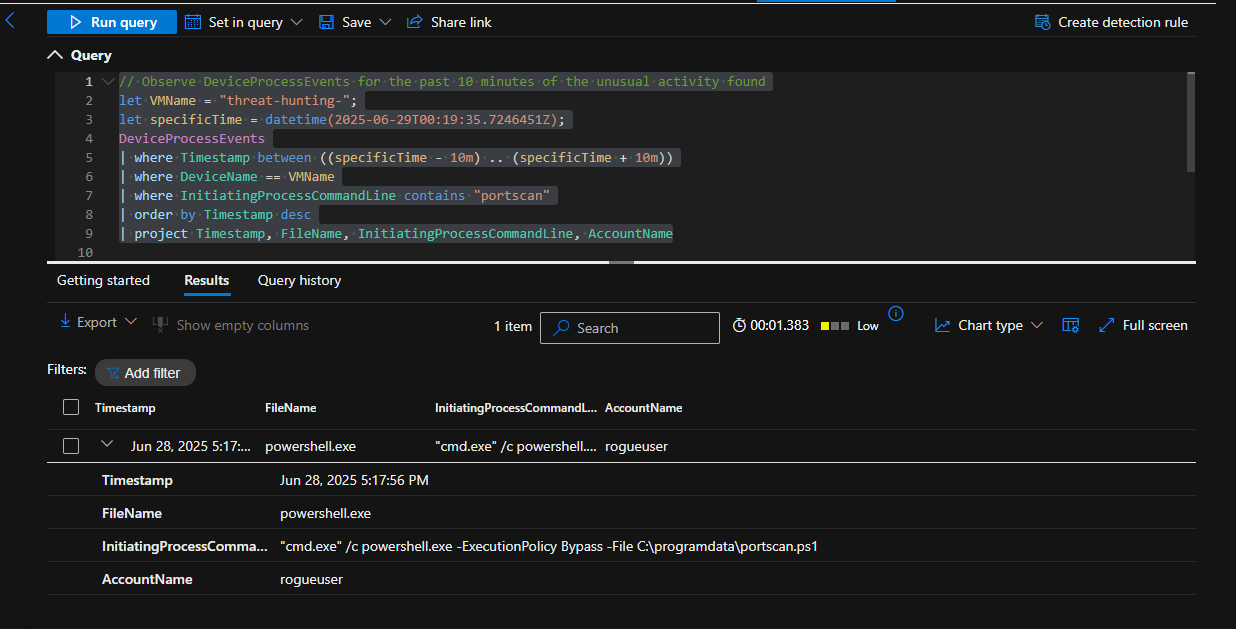
I searched for “portscan” and found the account name that ran portscan.ps1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// Observe DeviceProcessEvents for the past 10 minutes of the unusual activity found
let VMName = "threat-hunting-";
let specificTime = datetime(2025-06-29T00:19:35.7246451Z);
DeviceProcessEvents
| where Timestamp between ((specificTime - 10m) .. (specificTime + 10m))
| where DeviceName == VMName
| where InitiatingProcessCommandLine contains "portscan"
| order by Timestamp desc
| project Timestamp, FileName, InitiatingProcessCommandLine, AccountName
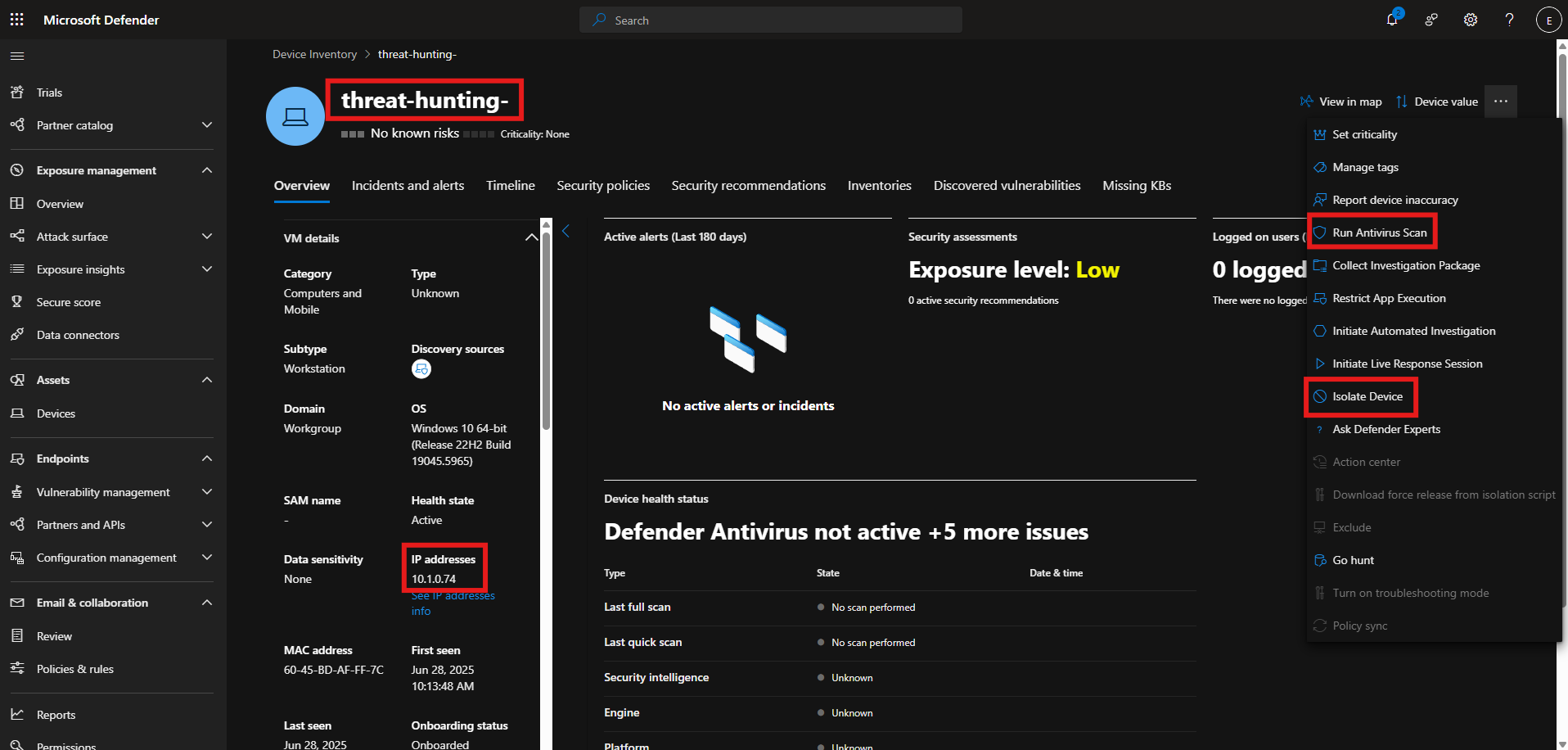
We observed the port scan script that was launched by the rogueuser account. This is not expected behavior from that account and was not something set up by administrators, so I isolated the device, and ran a malware scan.
The malware scan produced no results, so out of caution, we kept the device isolated and put in a ticket to have it re-imaged and rebuilt.
MITRE ATT&CK Framework Related TTPs
Based on your detailed threat hunting observations, here are the relevant MITRE ATT&CK Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) associated with the activity:
🧠 Key Behaviors Identified
- A rogue account (
rogueuser) ran a custom PowerShell port scanning script (portscan.ps1). - Multiple sequential connection failures to internal hosts were observed.
- The scan was stealthy in nature (no multithreading), likely intended to avoid detection.
- The device was isolated and scanned for malware (no malware detected).
🎯 MITRE ATT&CK Mappings
1. Tactic: Discovery (TA0007)
Technique: Network Service Scanning (T1046)
- The PowerShell script explicitly scans a list of common ports on internal IPs to determine which services are exposed.
- The sequential nature of failed connections is consistent with manual or scripted scanning behavior.
2. Tactic: Execution (TA0002)
Technique: Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell (T1059.001)
- The attacker used a PowerShell script to execute the scanning logic.
Test-NetConnectionand logging functions were invoked through a PowerShell command line.
3. Tactic: Credential Access (TA0006) (potentially, depending on further activity)
Technique: Valid Accounts (T1078)
- The use of the
rogueuseraccount to run the script suggests the possibility of compromised or misused credentials, especially since this behavior was not approved.
4. Tactic: Defense Evasion (TA0005) (conditional/optional)
Technique: Masquerading (T1036)
- If the
portscan.ps1script or its logs were made to appear like legitimate admin scripts (e.g., logging toC:\ProgramData), it may indicate basic evasion techniques.
Mitigations
🛡️ 1. Preventive Controls
🔐 Account and Identity Hardening
- Restrict local admin rights: Ensure that the
rogueuseraccount (and others like it) have only the minimum privileges required. - Enforce strong authentication: Use MFA for all privileged accounts.
- Monitor for lateral movement credentials: Disable unused accounts and enforce password hygiene.
🧾 Script and Execution Controls
- Constrain PowerShell usage:
- Enable Constrained Language Mode for untrusted users.
- Use AppLocker or Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC) to block unauthorized PowerShell scripts like
portscan.ps1.
- Disable PowerShell V2 if not needed: It lacks important security logging and is often abused by attackers.
🌐 Network Controls
- Segment internal networks: Apply strict firewall rules between subnets to reduce the impact of lateral scans.
- Limit ICMP and port access between workstations: Prevent Test-NetConnection from being effective across segments.
🔍 2. Detective Controls
🧭 Monitoring and Threat Hunting
- Log and alert on PowerShell execution:
- Enable PowerShell Script Block Logging and Module Logging in Group Policy.
- Look for
Test-NetConnection,ForEach, or custom script references likeportscan.ps1.
- Detect internal port scanning:
- Create detection rules for high volumes of connection failures in a short time frame.
- Alert when sequential ports or multiple hosts are targeted from a single endpoint.
📊 Sample Sentinel Analytics Rule (KQL)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
kql
CopyEdit
DeviceNetworkEvents
| where ActionType == "ConnectionFailed"
| summarize FailedCount = count(), DistinctPorts = dcount(RemotePort), DistinctHosts = dcount(RemoteIP)
by DeviceName, bin(Timestamp, 10m)
| where FailedCount > 100 and DistinctPorts > 10 and DistinctHosts > 5
🔧 3. Corrective and Recovery Actions
🧼 Incident Response
- Isolate and reimage the compromised device.
- Revoke credentials associated with the
rogueuseraccount and force password resets for other potentially exposed accounts.
📁 Post-Mortem & Lessons Learned
- Conduct a root cause analysis to determine:
- Was the account compromised or misused?
- Did the attacker gain persistence or try to exfiltrate data?
- Implement a SOAR (Security Orchestration Automation and Response) playbook to respond faster to similar patterns.
🧰 Recommended Tooling
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE): Can block suspicious PowerShell and log detailed activity.
- Sysmon: For rich endpoint logging, especially around script execution.
- Azure Sentinel / Microsoft Sentinel: Centralize and correlate logs with behavioral analytics.
✅ Summary Table
| Layer | Control | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoint | AppLocker / WDAC | Block unapproved scripts |
| Identity | Least privilege + MFA | Prevent misuse of accounts |
| Network | Segmentation + internal firewall rules | Limit scanning surface |
| Logging | PowerShell logging + MDE + Sentinel alerts | Detect script execution and port scans |
| Response | Isolation + reimaging + account revocation | Contain and remediate threats |